Your cart is currently empty!
Ringworm Infections
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but rather by a type of fungus. It’s a common and contagious fungal infection of the skin, scalp, or nails. The medical term for ringworm is dermatophytosis.
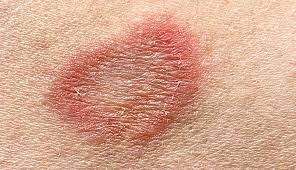
Causes: Ringworm is caused by various types of fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or object. Common fungi responsible for ringworm infections include Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton.
Symptoms: The symptoms of ringworm vary depending on the location and severity of the infection, but they often include:
- Red, scaly, or itchy patches on the skin
- Circular or ring-shaped rash with raised edges
- Clearing of the center of the rash, giving it a ring-like appearance
- Blistering, oozing, or crusting of the affected area
- Hair loss or brittle nails in cases of scalp or nail involvement
- Itching, burning, or discomfort
Types of Ringworm Infections:
- Tinea Corporis: Ringworm of the body affects the skin on various parts of the body, excluding the scalp, groin, and feet.
- Tinea Capitis: Ringworm of the scalp affects the scalp and hair follicles, leading to hair loss, scaling, and inflammation.
- Tinea Cruris: Also known as jock itch, ringworm of the groin affects the skin in the groin area, inner thighs, and buttocks.
- Tinea Pedis: Also known as athlete’s foot, ringworm of the foot affects the skin between the toes and the soles of the feet, causing itching, scaling, and cracking.
- Tinea Unguium: Also known as onychomycosis, ringworm of the nails affects the toenails or fingernails, causing thickening, discoloration, or crumbling of the nails.
Treatment: Treatment for ringworm typically involves antifungal medications, which may be applied topically (in the form of creams, lotions, or powders) or taken orally (in the form of tablets or capsules). Common antifungal medications include clotrimazole, miconazole, terbinafine, and griseofulvin. In addition to medication, practicing good hygiene, keeping the affected area clean and dry, and avoiding sharing personal items (such as towels, clothing, or sports equipment) can help prevent the spread of ringworm.